introduction
HACCP Plan – The Ultimate Guide
Food safety is essential for all food businesses. The HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) plan is a recognized system aimed at preventing foodborne hazards and ensuring compliance with HACCP certification standards. A properly implemented HACCP plan allows businesses to meet food safety regulations, maintain quality, and build consumer trust.
In this guide, we will cover every aspect of a HACCP plan, including its 7 principles, how to create one, example and answers of common questions.

📌 Learn More: HACCP vs. ISO 22000 – Key Differences
What is a HACCP Plan?
A HACCP plan systematically identifies, evaluates, and controls food hazards in the industry biological, chemical, and physical hazards. It ensures food safety from the very beginning with raw materials all the way to the final product. Companies seeking HACCP certification need to implement a thorough HACCP plan.
📌 HACCP Principles & Application Guidelines – FDA
Benefits of a HACCP Plan
- Ensures food safety by eliminating foodborne hazards.
- Facilitates compliance with FSSAI, ISO 22000, and USDA HACCP certification standards.
- Reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses and ensures product safety.
- Minimizes product recalls and enhances process efficiency.
- Boosts business reputation and expands market opportunities.
7 Principles of HACCP
The 7 principles of HACCP form the foundation of a food safety management system:
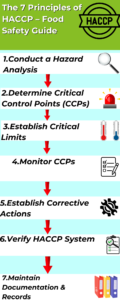
1. Conduct a Hazard Analysis
Identify biological (bacteria, viruses), chemical (pesticides, allergens), and physical (glass, metal fragments) hazards in food processing.
Example: In a dairy facility, microbial testing is crucial to detect Listeria monocytogenes in raw milk.
2. Determine Critical Control Points (CCPs)
Pinpoint key steps where hazards can be prevented, eliminated, or minimized.
Example: Pasteurization in milk processing eliminates Salmonella and E. coli.
3. Establish Critical Limits
Set acceptable safety limits (e.g., temperature, pH, time) for each CCP.
Example: Cook chicken to a minimum internal temperature of 75°C to ensure safety.
4. Implement Monitoring Procedures
Develop a routine for checking CCPs to ensure they remain within critical limits.
Example: Use temperature probes to monitor cooking temperatures and keep digital records.
5. Establish Corrective Actions
Define steps to take if critical limits are exceeded.
Example: If the refrigeration temperature rises above 5°C, either discard perishable items or transfer them to a backup unit.
6. Implement Verification Procedures
Regularly review the HACCP plan to ensure effectiveness through audits and testing.
Example: Conduct microbiological tests on food samples and validate cooking methods.
7. Maintain Documentation and Record-Keeping
Keep detailed records of hazard analyses, CCP monitoring, and corrective actions.
Example: Maintain sanitation logs, temperature records, and audit reports for compliance.
How to Develop a HACCP Plan (Step-by-Step Guide)
Step 1: Assemble the HACCP Team
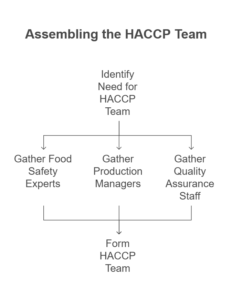
Gather food safety experts, production managers, and quality assurance staff.
Step 2: Describe the Product & Its Intended Use
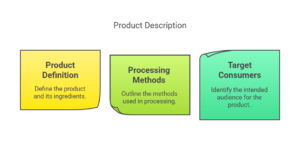
Define the product, ingredients, processing methods, and target consumers.
Step 3: Identify Hazards & Critical Control Points (CCPs)
Conduct a hazard analysis to determine necessary control measures.
Step 4: Establish Critical Limits & Monitoring Procedures
Define safety limits and create a monitoring system (e.g., temperature logs, microbial testing).
Step 5: Implement Corrective Actions & Verification Methods
Take corrective actions if a CCP is not met and conduct HACCP certification renewals.
Step 6: Maintain Proper Documentation & Record Keeping
Keep records such as:
- CCP monitoring logs
- Corrective action reports
- Audit and verification results
HACCP Plan Example (For a Food Business)
HACCP Plan for Pasteurized Milk Production
- 1. Product Description
Product Name: Pasteurized Milk Pasteurized Milk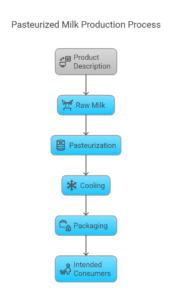
- Ingredients: Raw milk
Processing Methods: Pasteurization, cooling, packaging
Intended Consumers: General public - 2. Flow Diagram of Process Steps
Receiving raw milk
Storage at 4°C
Pasteurization (Heat treatment at 72°C for 15 sec)
Cooling to 4°C
Packaging
Storage and distribution - 3. Hazard Analysis & Critical Control Points (CCPs)
-
Process Step Potential Hazard Control Measure CCP? Receiving raw milk Biological: Bacteria (Salmonella, Listeria) Supplier audits, microbial testing No Storage Biological: Bacterial growth due to improper cooling Maintain temperature at 4°C Yes (CCP-1) Pasteurization Biological: Pathogen survival (Salmonella, E. coli) Heat milk to 72°C for 15 sec Yes (CCP-2) Cooling Biological: Recontamination due to improper cooling Rapid cooling to 4°C Yes (CCP-3) Packaging Physical: Foreign material contamination Use sealed, sanitized packaging No Storage & Distribution Biological: Bacterial growth if temperature exceeds 4°C Refrigerated transport & monitoring Yes (CCP-4) - 4. Critical Limits & Monitoring Procedures
CCP-1 (Storage Temperature): Maintain at ≤ 4°C (Check every 2 hours)
CCP-2 (Pasteurization): Heat to 72°C for 15 sec (Continuous monitoring with temp recorder)
CCP-3 (Cooling): Cool to ≤ 4°C within 2 hours (Monitor with temp log)
CCP-4 (Storage & Transport): Maintain ≤ 4°C (Use data loggers for monitoring) - 5. Corrective Actions
If storage temp exceeds 4°C → Discard milk or reprocess it
If pasteurization temp is not met → Hold batch & reprocess
If cooling time is exceeded → Investigate equipment & discard unsafe milk
If transport temp exceeds limit → Investigate cause, hold the batch, or recall if necessary - 6. Verification Procedures
Internal audits every 6 months
Microbial testing of pasteurized milk
Review temperature logs & corrective actions - 7. Record-Keeping
Temperature logs for storage, pasteurization, and transport
Corrective action reports for any deviations
Verification records from audits & test results
This HACCP Plan Example ensures that milk processing meets food safety regulations and adheres to HACCP certification standards like ISO 22000 and FSSAI.
Common HACCP Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
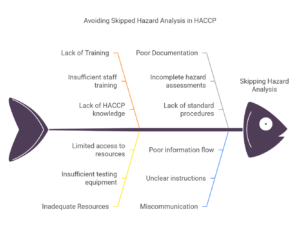
🚫 Skipping Hazard Analysis → Always perform a thorough risk assessment before putting HACCP into action. Example: Not testing raw milk for Salmonella prior to processing.
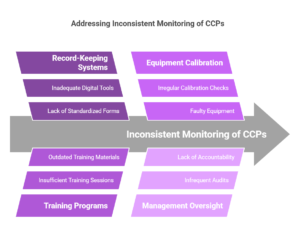
🚫 Inconsistent Monitoring of CCPs → Establish a reliable record-keeping system. Example: Failing to consistently log pasteurization temperatures.
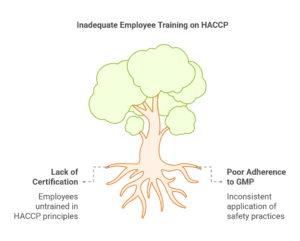
🚫 Lack of Employee Training → Ensure staff receive HACCP certification training. Example: Employees not adhering to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
🚫 Not Updating the HACCP Plan → Make it a point to review and update the plan annually or whenever new hazards are identified. Example: Introducing a new ingredient without revising the hazard analysis.

FAQs on HACCP Plan
General HACCP Information
What is a HACCP plan?
A systematic approach to identifying, evaluating, and controlling food safety hazards.
Why is HACCP important?
It ensures food safety, regulatory compliance, and consumer protection.
What are the 7 HACCP principles?
Hazard analysis, CCP identification, critical limits, monitoring, corrective actions, verification, and record-keeping.
What is the difference between HACCP and ISO 22000?
HACCP is a food safety system, while ISO 22000 is a broader food safety management system incorporating HACCP principles.
What is the difference between HACCP and GMP?
GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) focuses on overall hygiene and facility conditions, while HACCP is a hazard prevention system.
HACCP Certification & Compliance
Who needs HACCP certification?
Food manufacturers, processors, restaurants, catering services, and other food-related businesses.
Is HACCP mandatory?
Yes, in industries like meat, seafood, dairy, and juice processing, and recommended for all food businesses.
How long is HACCP certification valid?
Typically 1 to 3 years, requiring periodic audits for renewal.
How much does HACCP certification cost?
Costs vary depending on the certification body, business size, and industry requirements.
Can I get HACCP certification online?
Yes, many organizations offer online HACCP certification courses and exams.
Developing and Implementing a HACCP Plan
How do I create a HACCP plan?
By conducting a hazard analysis, identifying critical control points (CCPs), setting critical limits, and implementing monitoring procedures.
How do I determine Critical Control Points (CCPs)?
Use a decision tree to identify where hazards can be controlled in the production process.
What is a HACCP flow diagram?
A visual representation of all steps in food processing, showing where hazards may occur.
How often should a HACCP plan be updated?
Regularly, especially when changes occur in processes, ingredients, or regulations.
HACCP in Different Industries
What industries require HACCP?
Food processing, catering, hospitality, dairy, meat, seafood, beverages, and retail food sectors.
Do restaurants need HACCP?
Yes, HACCP helps restaurants maintain food safety and comply with health regulations.
What is the role of HACCP in food packaging?
It prevents contamination and ensures safe storage and transportation of packaged foods.
How does HACCP apply to beverage manufacturing?
It controls hazards like microbial growth, chemical contamination, and packaging safety.
Can HACCP be applied to organic food production?
Yes, HACCP ensures safety while maintaining organic standards.
HACCP Audits & Compliance Challenges
What is a HACCP audit?
An inspection to verify that a food business is following its HACCP plan correctly.
What are common HACCP non-conformities?
Lack of proper documentation, inadequate monitoring, poor corrective actions, and failure to train staff.
How can I prepare for a HACCP audit?
Maintain up-to-date records, train employees, conduct internal audits, and ensure compliance with all CCPs.
What happens if a HACCP plan is not followed?
Businesses may face regulatory penalties, food recalls, and reputational damage.
How does HACCP help with food recalls?
It minimizes the risk of contamination and ensures traceability, making recalls more efficient.
Technology & Advanced HACCP Applications
What are some HACCP software tools?
FoodDocs, Safefood 360, and HACCP Builder help businesses manage HACCP documentation.
How does HACCP integrate with ISO 9001?
HACCP focuses on food safety, while ISO 9001 ensures overall quality management. Both can be combined for better compliance.
What are the biggest challenges in HACCP implementation?
Employee training, proper documentation, identifying CCPs, and ensuring continuous monitoring.
Conclusion
A HACCP plan is crucial for ensuring food safety and meeting regulatory requirements. By adhering to the 7 principles of HACCP, businesses can effectively identify and manage potential hazards. Implementing a HACCP plan not only guarantees safe food production but also builds consumer trust and facilitates regulatory approval.
Would you like a customized HACCP plan template for your business? Share your thoughts in the comments!
If you’d like to read about FSSAI, please visit our article [here].

Pingback: FSSAI License Renewal: Online Process, Fees & Required Documents -
Pingback: Food Safety Management System: A Proven Path to Safer & High-Quality Food
Pingback: Food Safety vs. Food Hygiene: What’s the Difference and Why Does It Matter? - foodtechzone
Pingback: FSSAI Registration Process: Complete Guide (2025) - foodtechzone